CNC Milling
High-Precision Prototyping & Production
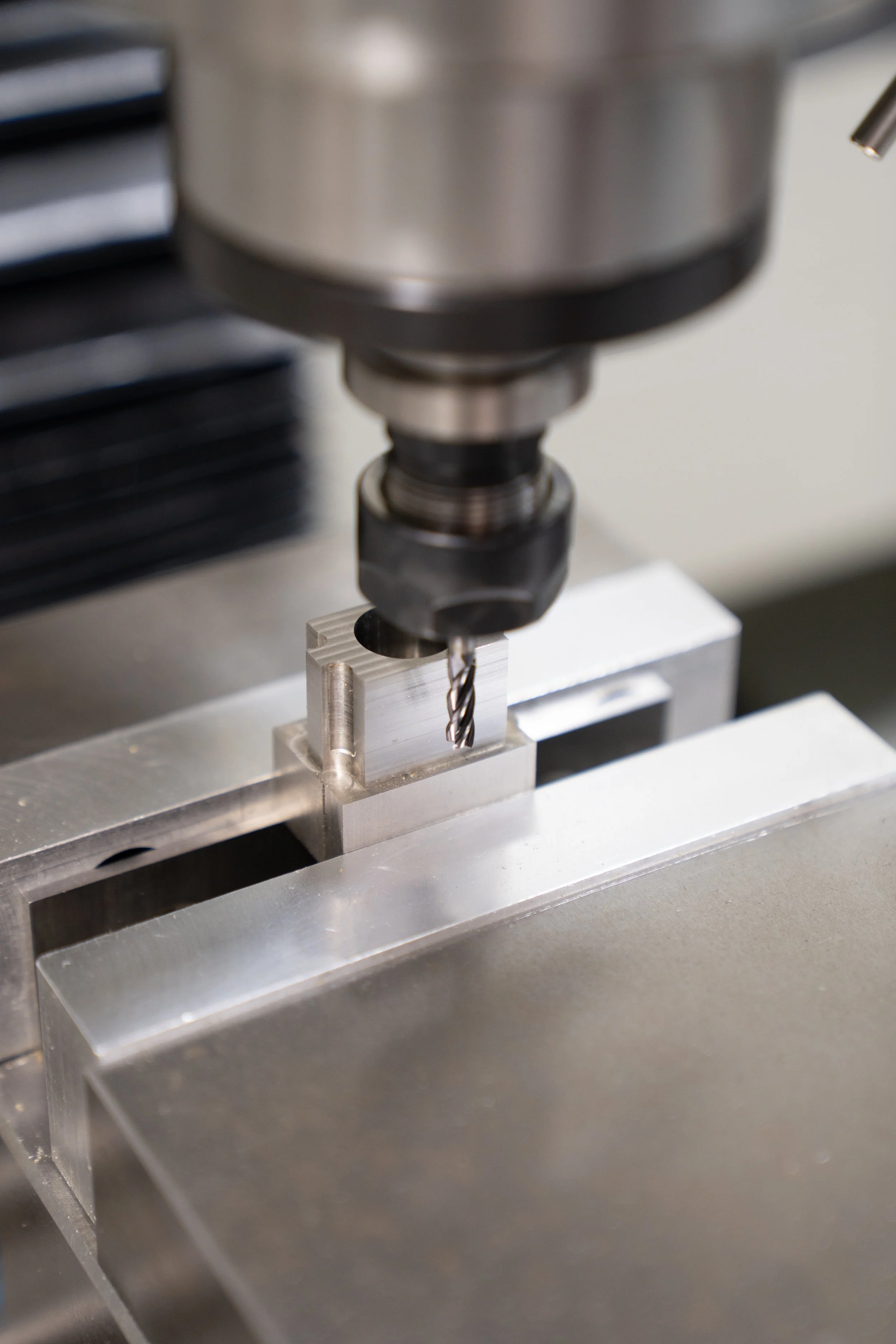
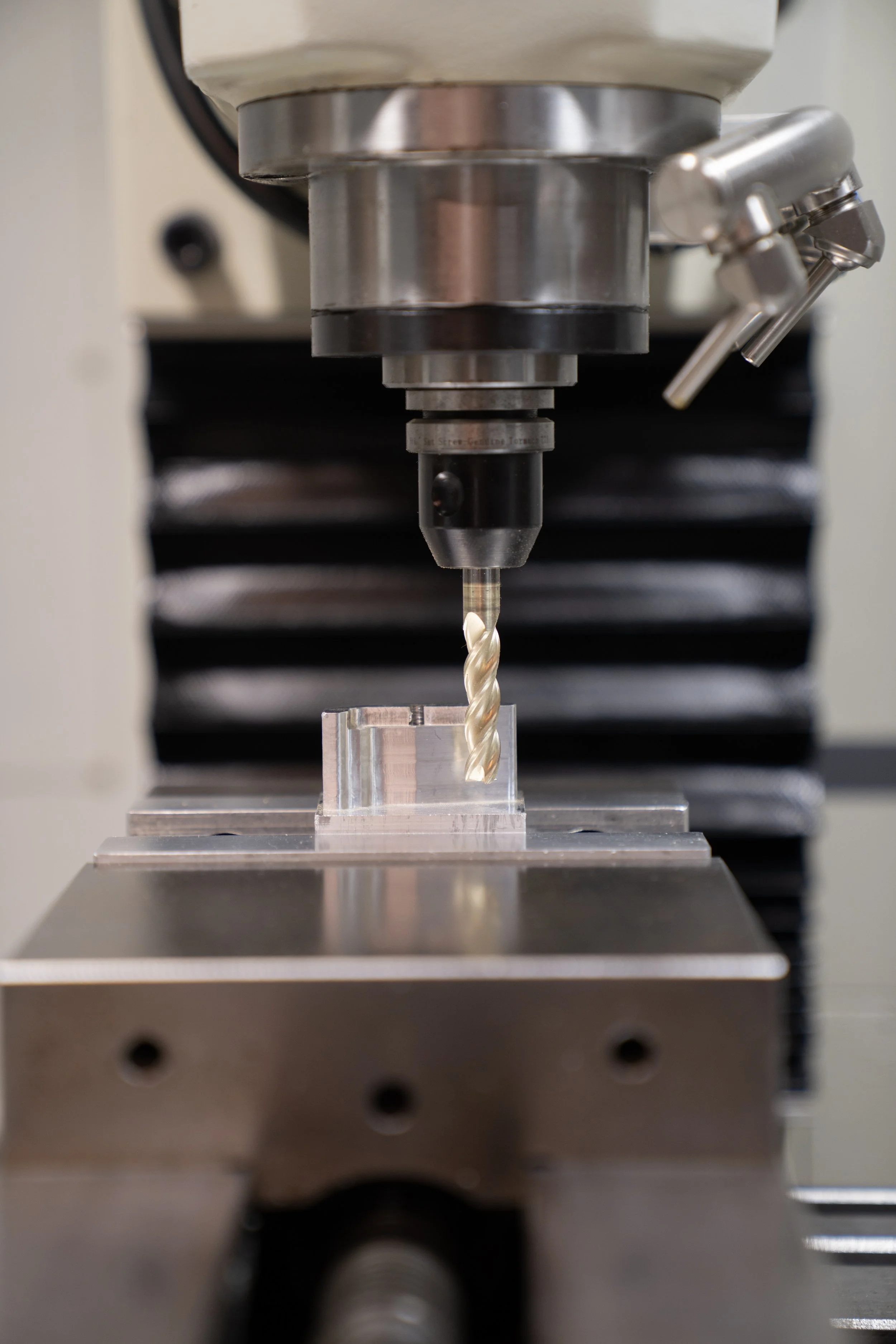
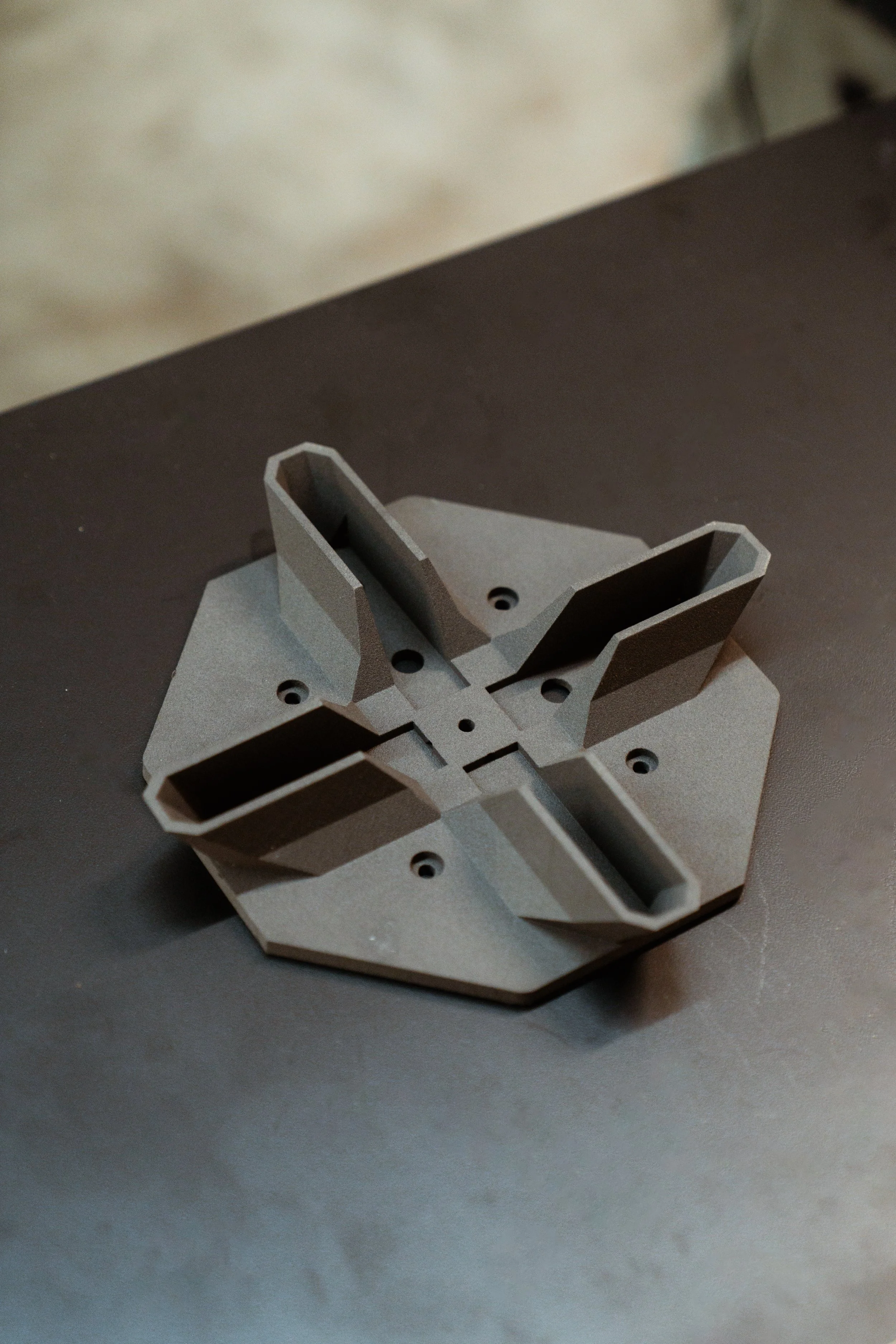
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a precision machining process that uses a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a workpiece based on a computer-programmed design. This technique allows for highly accurate, repeatable, and complex part production, making it ideal for prototyping, low-volume production, and custom components across industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and manufacturing.
Why Choose CNC Milling?
-
Produces parts with tight tolerances within a few thousandths of an inch.
Ensures high repeatability, maintaining consistency across multiple parts.
-
Once programmed, CNC milling enables fast, automated production.
Reduces human error, allowing for efficient, consistent machining.
-
Works with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Allows for complex geometries that traditional machining cannot achieve.
-
Enables low-volume production for custom and specialized components.
Supports functional prototypes that closely resemble final production parts.
How CNC Milling Works
-
Design
The process begins with a digital 3D model created in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design is then converted into G-code, which serves as the machine's instructions.
-
Setup
The workpiece, whether metal, plastic, or composite, is clamped securely onto the milling table. The appropriate cutting tool is inserted into the spindle.
-
Machining
The CNC mill follows the G-code instructions, precisely controlling tool movement, feed rate, and cutting speed to remove material and shape the part.
-
Finishing
Once the part is machined, it may undergo sanding, polishing, painting, or other post-processing for enhanced functionality and aesthetics.
Key CNC Mill Components
✔ Spindle – Rotates the cutting tool at high speeds.
✔ Cutting Tools – Available in various shapes and sizes for different tasks.
✔ Work Table – Secures the workpiece during machining.
✔ Axes – Typically operates on three axes (X, Y, Z), with advanced mills incorporating additional axes for complex movements.
✔ Computer Control – Converts G-code into precise machine movements.
Materials Available for SLS
-
Aluminum
Stainless Steel
Steel
Various Metal Alloys
-
ABS
ADPE/UDHPEAcetal
Nylon
Garolite
Polypropylene
Peek
PTFE
Maximum Part Size: 15 inches x 9 inches x 16 inches
Most Common Part Size: 6 inches x 6 inches x 6 inches
Precision: Tight tolerances within a few thousandths of an inch
High Repeatability: Ensures consistency across multiple production runs
Machine Capabilities
Industries & Applications
-
Why CNC Milling? High precision, durability, and material versatility.
Examples: Brackets, housings, structural components.
-
Why CNC Milling? CNC mills can produce one-off or batch production of precision fixtures.
Examples: Custom brackets, jigs, and industrial tooling for manufacturing and assembly lines.
-
Why CNC Milling? Ensures tight tolerances and material flexibility for prototype testing.
Examples: Single-run metal or plastic prototypes for product development.
-
Why CNC Milling? Enables the creation of complex geometries in high-strength materials.
Examples: Small high-accuracy components for machinery or custom assemblies.ment Company